This guide is written specifically for HR managers, founders, and decision-makers who need a clear understanding of Labour Act 2074 Nepal for Employers. Hiring employees in Nepal is not just about filling roles. It’s about building a legally compliant, trusted, and sustainable workplace. Whether you’re a startup founder in Kathmandu, an HR manager in Pokhara, or a growing hospitality business in Chitwan, understanding the Labour Act 2074 (Shram Ain 2074) is essential.
This employer-focused guide explains how Nepal’s labour law affects hiring, contracts, SSF, working hours, leave, wages, and termination, with practical checklists you can apply immediately.
Labour Act 2074 – Employer Compliance at a Glance
Quick Summary for Employers
- Written employment contract is mandatory
- Probation period: up to 6 months
- Working hours: 8 hours/day, 48 hours/week
- Overtime: max 24 hours/week at 1.5× pay
- SSF registration: from the joining date
- Minimum wage compliance required
- Legal grounds + notice required for termination
Why Labour Law in Nepal Matters for Hiring

Imagine you’ve just founded a fast-growing startup in Kathmandu or you’re heading HR at a hospitality business in Pokhara. You want to bring in reliable talent, but you also know that Nepal’s labour law isn’t something you can ignore. Mistakes can lead to fines, disputes, and reputational damage.
Labour compliance should be built into each stage of hiring. For a step-by-step hiring flow, see 8 Simple Steps to a Successful Recruitment Process in Nepal.
Nepal’s Labour Act 2074 sets the minimum legal standards for:
- Employment agreements
- Working hours and overtime
- Wages and increments
- Leave and holidays
- Social Security Fund (SSF)
- Termination and retrenchment
Employers planning long-term roles should also understand the legal framework behind permanent hiring, which we explain in our guide on Direct Hire in Nepal – What It Means and Why It’s Beneficial.
What is SSF? (Social Security Fund Explained for Employers)
The Social Security Fund (SSF) is Nepal’s long-term social protection system for employees. Both employer and employee contribute a percentage of their monthly salary, which supports:
- Retirement and pension
- Medical treatment
- Disability coverage
- Maternity and dependent benefits
- Unemployment support
For employers, SSF compliance is more than a legal requirement. It’s a trust signal. Companies that deposit SSF on time attract better candidates and experience lower attrition.
Why SSF matters for employers:
- Mandatory under Labour Act 2074
- Protects the company during inspections or audits
- Builds employee trust and retention
- Reduces future disputes
Key Provisions of Labour Act 207
Types of Employment Under Labour Act 2074
| Employment Type | Description | SSF Required | Duration |
| Regular | Permanent employees | Yes | Unlimited |
| Time-bound | Fixed-term contract | Yes | Fixed term |
| Work-based | Project-specific | Yes | Until completion |
| Part-time | Under 35 hrs/week | Yes (proportional) | Unlimited |
| Casual | Irregular/short-term | Yes | Short-term |
| Trainee/Intern | Learning-based | Yes | Up to 1 year |
Probation Period Rules
- Maximum probation period: 6 months
- Must be clearly stated in the contract
- If performance is satisfactory, employment continues as regular
Structured probation reviews and documentation are also part of best recruitment practices for Nepalese employers, helping reduce disputes later.
Working Hours & Overtime Rules
| Rule | Requirement |
| Daily Working Hours | 8 hours |
| Weekly Working Hours | 48 hours |
| Overtime Limit | 24 hours/week |
| Overtime Rate | 1.5× salary |
| Break Requirement | 30 mins after 5 continuous hours |
Leave & Holidays Under Labour Act 2074
| Leave Type | Entitlement | Accumulation |
| Home Leave | 1 day/20 days worked | 90 days |
| Sick Leave | 12 days | 45 days |
| Maternity Leave | 14 weeks | No |
| Paternity Leave | 15 days | No |
| Mourning Leave | 13 days | No |
| Public Holidays | As per govt | No |
Wages, Salary & Minimum Pay
- Employers must follow the government-declared minimum wage
- Salary is generally paid monthly for regular employees
- Annual increment: at least half-day salary after one year of service
- Deductions must be transparent and legal
SSF Contributions (Employer Responsibility)
- SSF registration from the actual joining date
- Monthly contributions by both employer and employee
- Late or missed deposits are a major compliance risk
Termination & Retrenchment Rules
- Termination must have valid legal grounds (performance, health, redundancy, etc.)
- Proper notice period is mandatory
- Retrenchment compensation often equals one month’s salary per year of service
- Unfair termination can be challenged at the Labour Office or Labour Court
Health, Safety & Non-Discrimination
- Safety & health policy required (especially with 20+ employees)
- No discrimination based on caste, gender, religion, or origin
- Child labour and forced labour are strictly prohibited

Common Compliance Mistakes Employers Make
Based on real employer cases and worker experiences in Nepal:
- No Written Contracts – Verbal hiring leads to disputes
- Delayed or Missing SSF Deposits – One of the most common violations
- Illegal Training Bonds – Long trainee contracts without exit rights
- Overtime Without Records – Cash payments without logs
- Misclassifying Part-Time Staff – Avoiding SSF and leave obligations
- Improper Termination – No notice or documentation
Many of these legal issues stem from common hiring errors, discussed in detail in Recruitment Mistakes in Nepal: How Companies Can Improve Their Hiring Process.
Hiring Compliance Checklist for Employers (Labour Act 2074)
Before Hiring
- efine job role and employment type
- Prepare legal contract template
- Verify minimum wage compliance
- Plan working hours and weekly off
When Hiring
- Issue appointment letter
- Collect employee documents
- Register employee in SSF
- Explain leave and notice policies
- Set probation timeline
During Employment
- Maintain daily attendance
- Track overtime and breaks
- Update payroll monthly
- Deposit SSF on time
- Issue payslips
When Employee Leaves
- Verify notice period
- Prepare final settlement
- Update SSF records
- Provide an experience letter (recommended)
What Employers Should Do to Stay Compliant
Set Up a Hiring Compliance Checklist
- Always have a standard contract template (regular, part-time, trainee)
- Make sure probation period is clearly defined
- Include SSF clause, salary, leave, termination details
Track Working Hours & Overtime
- Use an attendance system
- Calculate any overtime carefully (max 24 hrs/week)
- Provide rest breaks (30 mins after 5 continuous hours)
Register Employees for SSF Immediately
- Do SSF registration at the start of employment
- Deduct and contribute as per law (both employer and employee)
- Regularly reconcile SSF contributions
Write & Enforce a Leave Policy
- Define weekly off, yearly holidays, sick leave, maternity leave
- Track leave accumulation (home leave, sick leave) per legal limits
Prepare for Termination Fairly
- Use clear performance metrics for probation
- Provide legal notice or severance if required
- Maintain documentation
Health, Safety & Non-Discrimination Policies
- Draft a workplace safety policy (workplace rules) if 20+ workers
- Have a mechanism for health & safety complaints
- Avoid discriminatory hiring or workplace practices
Educate Your Team
- Train your HR / Admin / Founders on key sections of Labour Act 2074
- Share a summary of compliance obligations
- Use external legal advisors if needed

Real-World Risk Scenarios in Nepal
Verbal Agreement Trap
Hiring without written contracts often leads to salary and notice disputes.
Unregistered Part-Time Workers
Part-time employees also require SSF enrollment (proportional).
Illegal Training Agreements
Training periods cannot exceed one year, and penalties must be fair.
Overtime Without Proof
Without attendance records, employers struggle to defend claims.
Late SSF Deposits
A common audit red flag and worker complaint.
Sudden Termination
Termination without notice or documentation creates legal exposure.
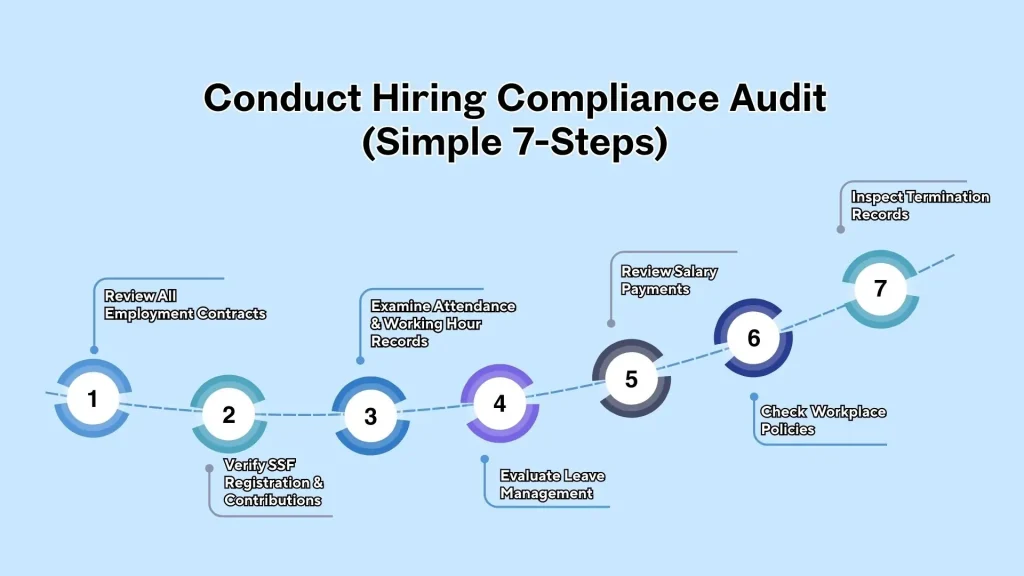
How to Conduct a Hiring Compliance Audit (7 Steps)
- Review all employment contracts
- Verify SSF registration and payments
- Check attendance and working-hour records
- Audit leave balances
- Review payroll and wage compliance
- Confirm workplace policies (20+ staff)
- Inspect termination documentation
Handling Disputes, Complaints & Inspections

- Address employee concerns early
- Maintain complete documentation
- Attempt internal resolution first
- Prepare transparently for labour inspections
- Follow Labour Office and Labour Court procedures if required
Follow Labour Office and Labour Court procedures if required
The Labour Act 2074 is available in both Nepali and English through official government sources. Employers should rely only on official versions for compliance reference.
Conclusion: Build a Fair, Compliant & Sustainable Workplace
Hiring compliance under the Labour Act 2074 is not a burden, it’s a business advantage.
By following the law and implementing structured HR systems, Nepali employers can:
By following the Labour Act 2074 and adopting good HR practices, you can:
- Avoid fines or legal disputes
- Improve employee trust
- Build a professional work culture
- Attract better talent
- Strengthen your brand as an employer
By following Labour Act 2074 Nepal for Employers, companies can reduce legal risk and build a sustainable workforce.
For more insights and updates related to hiring and other topics, explore TalentSathi’s Article page.
FAQs
How does labour Act Nepal regulate working hours and overtime?
The Act sets 8 hours/day, 48 hours/week, with mandatory breaks and higher overtime pay.
What are the SSF requirements under Labour Act 2074?
Employers must register employees in SSF and contribute monthly as per legal percentages.
How do I write an employee contract under Labour Act 2074?
Include job type, pay, hours, leave, probation, SSF details, and termination terms.
What termination rules apply under Labour Act 2074?
Employers need valid reasons, proper notice, and severance where applicable.
Where can I find Labour Act 2074 in Nepali (PDF)?
It’s available on official Nepal government and Nepal Law Commission websites.
What is Labour Act 2074 in Nepal?
It’s Nepal’s main employment law governing hiring, contracts, working hours, wages, leave, and termination.




